Dwarven Consonants
|
Place Of Articulation |
| Manner of Articulation |
Labial
(lips) |
Dental
(teeth) |
Palatovelar
(palate/roof of
mouth) |
Glottal
(vocal folds) |
| Bilabial |
Labio-dental |
Inter-dental |
Alveo-lar |
Alveo-palatal |
Palatal |
Velar |
|
| Stops: Voiceless |
|
|
|
t |
|
k k<h> |
? |
| Stops: Voiced |
b |
|
|
d |
|
g g<h> |
|
| Fricatives: Voiceless |
|
f |
T
thigh |
s |
S
shun |
|
h |
Fricatives:
Voiced |
|
|
|
z |
|
|
|
| Affricates: Voiceless |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Affricates:
Voiced |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nasals: |
m |
|
|
n |
|
|
|
Liquids:
Lateral |
|
|
|
l |
|
|
|
Aproximats
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
| Semivowels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
w |
|
This chart uses the Usenet suggested IPA ASCII
k<h>: repesents an aspirated k, as at the beginning of the English word "kick" vs an unaspirated k at the end of the word. To Dwarves two k sounds are seperate phonemes.
Dwarves only use the 5 basic vowels:
| a | sat |
| e | set |
| i | seat |
| o | sote |
| u | soot |
These vowels vary in length. A long vowel will be held twice as long as a short one.
Dwarven
| Cirth |
Number |
Phonetic Transcription |
English Equivalant Sound |
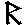 |
2 |
b |
tab |
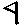 |
3 |
f |
fill |
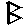 |
6 |
m |
mill |
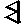 |
7 |
mb |
|
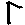 |
8 |
t |
tat |
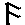 |
9 |
d |
tad |
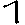 |
10 |
T (th) |
thigh |
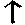 |
12 |
r |
rill |
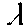 |
15 |
S (sh) |
shlling |
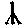 |
17 |
z |
godzilla |
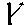 |
18 |
k |
pick |
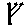 |
19 |
g |
pig |
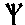 |
22 |
n |
nil |
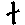 |
31 |
l |
lily |
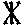 |
33 |
nd |
and |
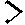 |
34 |
h |
hill |
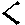 |
35 |
? (glottol stop) |
Oh oh! |
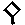 |
44 |
w |
will |
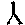 |
54 |
s |
sill |
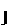 |
59 |
aspiration |
|
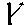 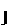 |
18,59 |
k<h> |
kill |
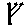 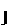 |
19,59 |
g<h> |
gill |
Vowels
| | Unrounded | | Rounded |
| | Front | Central | Back | | Front | Central | Back |
| High |
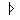 | i (tense) | beat |
| i" (reduced lax) | chicken |
|
|
|
|
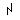 | u (tense) | shoe |
| Semi High |
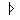 | I (lax) | bit |
|
|
|
|
|
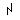 | U (lax) | put |
| Upper Middle |
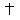 | e (tense) | bait |
|
|
|
|
|
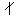 | o (tense) | boat |
| Middle |
|
| @ | sofa |
|
|
|
|
| | boy |
| Low Middle |
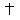 | E (lax) | bet |
|
| V (lax) | but |
|
|
|
| O | caught |
| Low |
| & (lax) | ash |
| a | park (Boston) |
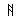 | A (lax) | pot |
|
|
|
|
Alphabet
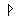
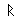
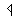
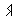
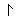
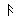
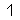
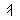
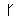
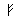
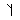
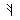
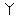
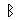
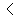
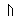
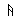
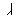
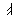
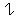
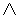
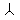
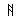
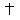
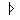
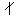
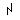
Roots
All roots have the form of RX - R - RY where:
X = Any consonant except "j" and "?" + any aproximant.
Y =
- Any nasal + Any consonant except "f", "j", and "?".
- Any aproxamant + Any consonant except "f", "j", and "?".
- Any stop + Any Fricative except "f".
R = X, Y, 0, or any single consonant except "f"
RX = X or 0 or any single consonant except "j" and "?".
RY = Y or 0 or any single consonant except "j" and "?".
No more than one radical of a word may be 0.
"j", "?" may only occur medially in the pattern "fleeting o"-C-"fleeting o".
The "fleeting o" is dropped if any other vowel exists in that position.
"f" may only occur initially or finally in the patterns: f-"fleeting o" or "fleeting o"-f.
The "fleeting o" is dropped if any other vowel exists in that position.
Word Formation
All words are formed from stems of consonants consisting of 3 radicals see roots.
These roots are not pronouncable words by themselves but used to derive
denotational words by the insertation of vowels, doubling of a consonant,
and addition of prefixes and suffixes.
Words are inflected by internal vowel changes, the radicals of the root remaining the
same (subject only to assimilation).
Parts of Speech
Denotational
- Noun- ma?al "smith", targ "beard", zarm "water". Nouns come in 3 genders: Animates, Items and Locations. each with unique properties.
Formation:
- Any noun: By the insertation of "a" between the 1st and 2nd and 2nd and
3rd (b-r-k: barak "axe") radicals if the last radical is a liquid (l or r).
- Any noun: By insertation of the letter "a" between the 1st and 2nd
radical (z-r-m: zarm "water" )
- Animate nouns with a meaning of someone who makes or does the basic noun from the same root are formed by the insertation of "a" between the 1st and 2nd radicals and the suffix "Un". These are only formed from Item roots: b-r-k -> barkun "axe maker
, weaponsmith".
- Animate nouns with a meaning of someone who uses the standard noun from the same root by the addition of the prefix "u" and the insertation of "a" betwee nthe 2nd and 3rd radicals. These are only formed from Item roots:
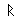 -
- 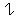 -
- 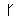 ->
-> 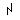
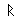
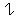
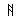
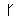 "axe weilder, solider".
"axe weilder, solider".
- Adjective- zirik "silver color", narag "black"
Formation:
- By th insertaion of "i"'s or "a"'s between each radical.
There is now way to determine wheather "i" or "a" is the correct vowel.
- Verb- meqel "to forge", nurug "to blacken"
- Adverb- Formed from adjectives
- Pronoun
- Numeral
Syntactical
- Prep
- Conjunction
- Particle -li in russian, zhe,
- Interjection
Assimilation
- In association with an aproximat or nasal all fricatives
assimilate to z.
- In association with any other consonant nasals assimilate to
the point of articulation of the other consonant.
- In association with an voiced consonant, nasal or aproximant
voice a voiceless consonant.
Phonological Constraints
"f", "j" and "?" do not occur in consonant clusters, the "fleeting o"
appears if during inflection they would become part of a consonant
cluster.
X = Any consonant except "j" and "?" + any aproximant.
Y =
- Any nasal + Any consonant except "f", "j", and "?".
- Any aproxamant + Any consonant except "f", "j", and "?".
- Any stop + Any Fricative except "f".
R = X, Y, or any single consonant except "f"
RX = X or any single consonant except "j" and "?".
RY = Y or any single consonant except "j" and "?".
+- -+ +- -+
|+- -+ | |+- -+ |
|| RX |1 | || R + V + RY | |
|+- -+ | || Y + (V) |1|
|+ - -+ | + V + |+- -+ |
|| (V) + X | | |+- -+ |
|| RX + V + R |2| || RY |2 |
| +- -+ | |+- -+ |
+- -+ +- -+
Cases
nom/acc/gen animate and locations
erg/abs/pos items
ergative case: Subject of transative verbs
absolutive case: Subject of intranative verbs and objects of transative verbs
dative: indirect objects, objects of certain verbs
locative: in or on
genative: possession
nomnative: subject
prepositional: w certain preps
vocative: direct address
Gender:
Animate
Locations
Itmes
Abstracts
Verbs
Tense
Perfection- Completed action
Aspects- ongoing, single, habitual, repeated
Mood- indicative, subjunctive, negative, imperative
Transative, Intransative, Reflexive
Static vs dynamic ride vs mount, reside ve settle
deference (Japanesse)
Person
Number
Personal pronouns
by gender in all persons not just 1st
singluar, dual, plural
inclusive and exclusive we
politeness
presence of 3rd persons
real and hypothetical
Adjectives
comparative and superlative
un-, -able, -less, -full, -phile, -phobe, -er, -an -ian, -ese, -ish
adverb -ly
Noun phrase order
Sentance order SVO etc
Question formation, how to form yes no question
How to negate a sentance
Conjunctions: XY-que
vel X vel Y (both X and Y) or (X or Y)
aut X aut Y either X or Y
Politeness
2nd person address, or title, caste
Stress
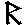
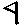
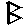
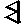
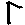
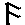
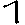
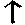
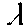
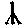
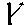
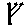
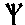
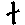
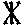

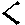
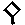
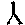
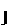
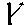
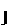
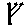
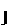
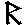
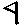
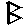
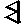
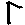
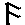
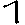
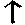
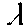
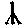
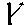
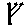
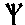
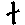
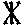

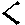
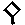
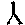
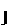
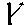
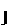
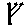
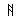
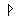
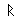
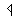
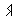
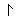
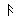
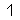
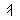
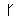
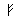
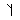
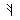
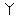
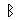
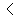
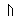
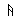
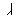
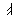
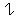
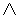
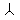
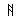
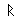 -
- 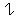 -
- 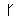 ->
-> 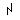
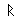
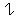
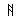
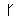 "axe weilder, solider".
"axe weilder, solider".